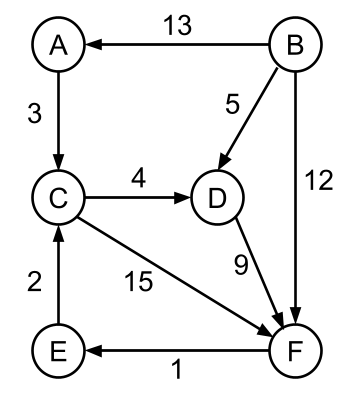
- d(B, C) = ?
- d(C, F) = ?
- d(E, A) = ?
Answer:
- d(B, C) = 15
- d(C, F) = 13
- d(E, A) = infinity
What happens if some edges are better than others?
A graph that has a numeric label w(e) associated with each edge e, called the weight of edge e.
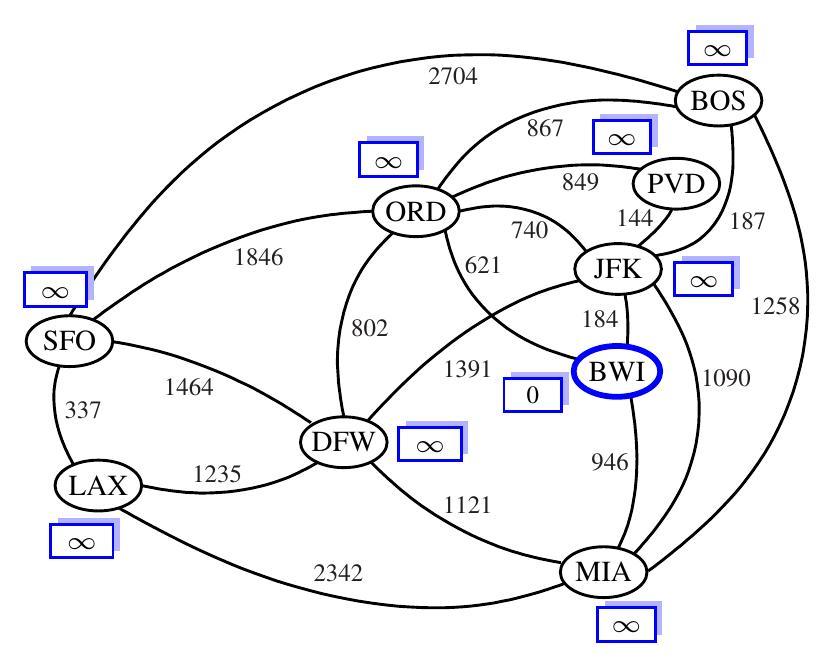
Here is a weighted graph whose vertices represent major US airports and whose edge weights represent distances in miles.
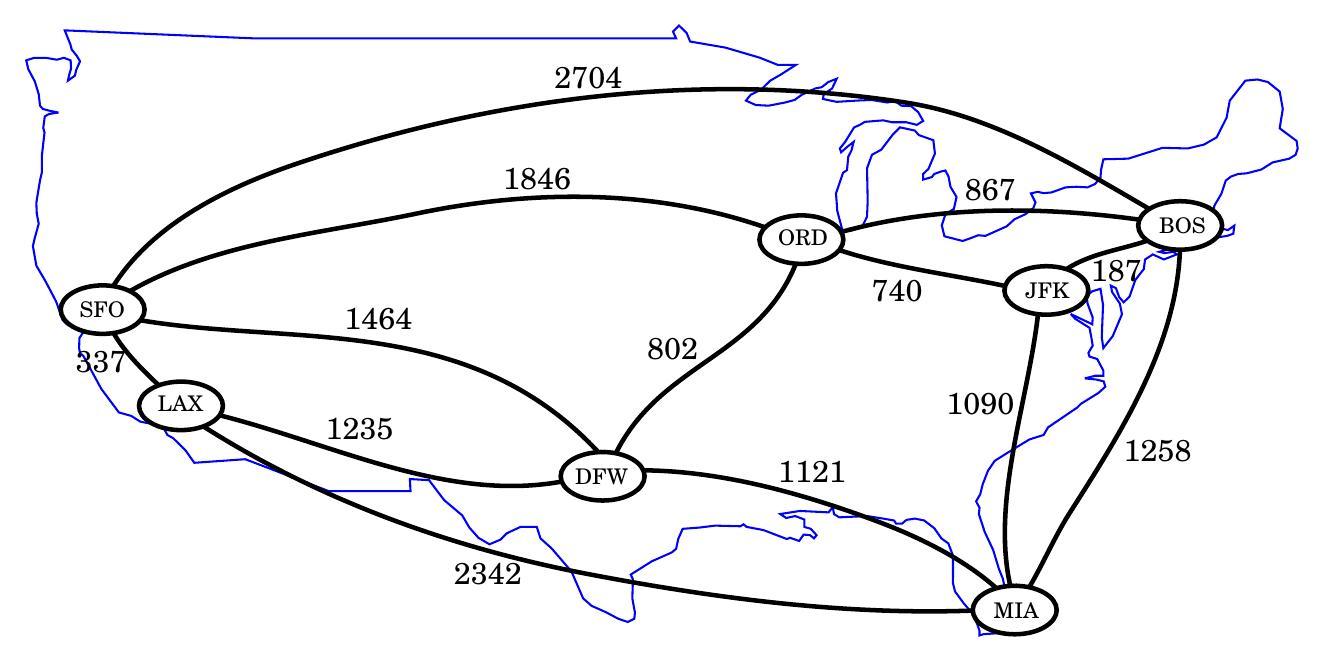
This graph has a path from MIA to SFO of total weight 2,585 (going through DFW). This is the minimum-weight path in the graph from MIA to SFO.
Answer: 2777, through DFW and ORD.
Let G be a weighted graph. The length (or weight) of a path P is the sum of the weights of the edges of P. The distance from a vertex u to a vertex v in G, denoted d(u, v), is the length of a minimum-length path (shortest path) from u to v. If there is no path from u to v, then d(u, v) is infinity.

Answer:
Algorithm Dijkstra(G, s):
Input: A directed or undirected graph G with nonnegative edge weights, and a distinguished vertex s of G
Output: The length of the shortest path from s to v for each vertex v of G
Initialize all vertices to have distance of infinity, except for s which is 0
Initialize a priority queue Q with all vertices using their distance as the key
while Q is not empty:
u = vertex in Q with smallest distance
remove u from Q
for each neighbor v of u:
if distance[u] + weight(u, v) < distance[v]:
distance[v] = distance[u] + weight(u, v)
Return distance
Click "Initialize..." to begin.